Oct 25, 2024
Cell culture is a process of growing cells outside their natural environment, like growing human cells outside a human body. For this, it is needed to isolate the human cells of a specific tissue, nurture them, and control their environment and conditions. Those factors help the cells grow and, therefore, accelerate their development.
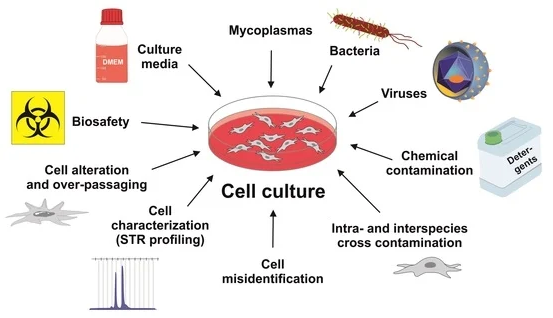
Some essential conditions that cells of cell culture are subjected to are:
Controlled Environment: The incubator's temperature, what kind of incubator it is, whether it uses CO2 (which is not necessary to grow it), and even humidity.

Nurture: Cells need to grow, so they must consume some 'food.' That means they need to be nurtured. A different medium is necessary for each cell, such as Fetal bovine serum (FBS), a centrifuged and filtered liquid extracted from fetal bovine blood.

Aseptic Techniques: Cultivating the cells in a clean and aseptic place is vital. This differs from growing bacteria or fungi because they need less protection and are less delicate. Antibiotics and antifungals must be administered, such as ampicillin, streptomycin, or gentamicin. The cells must also be filtered often, and their flasks must be changed.

To culture cells, you need to consider the cell types. This includes primary cells, which are isolated from tissue; immortalized cell lines, which are immortalized cells that can divide indefinitely, such as HEK293; and stem cell lines, which are cells that can self-renew or turn into distinct cell types due to the signals they receive from the body.
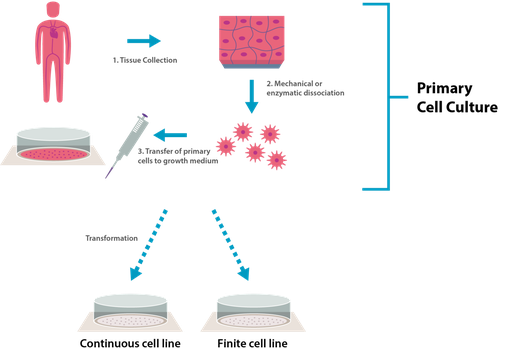
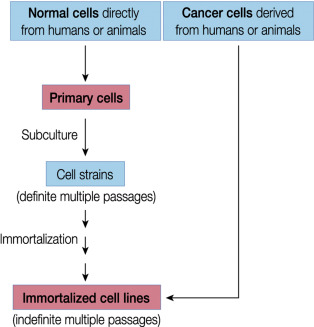
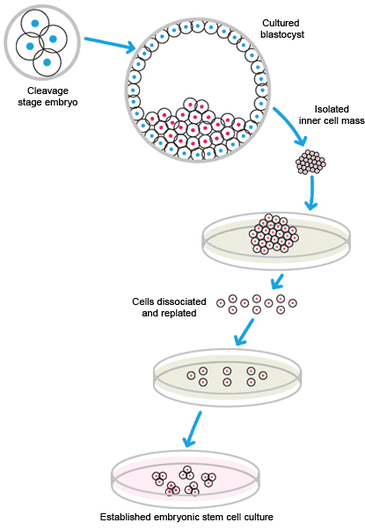
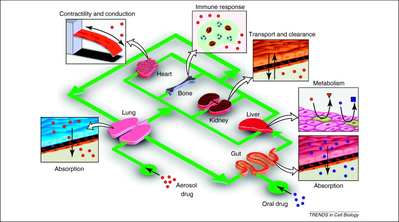
Cell culture can help people in biological research. This is because it can help people study the behavior of the cell, drug discovery and development (using the cells as a test for drugs or for developing some treatment), vaccine production, tissue engineering (creation of artificial tissue, for example, artificial organs), and genetic engineering (to study the function of the gene or do gene therapy).
However, regarding the uses of cell culture, which were previously cited, they have not developed the complexity of a living organism. That is why exit tests are done in vitro and in vivo. The reliability can be decreased over time due to the mutations the cultured cell line can suffer, thus changing their behavior. They are delicate, so bacteria and fungi can easily contaminate your culture and compromise the goal of the culture. It is expensive and difficult to administer as a large-scale production. This is one of the reasons for the difficulty of producing large-scale meat using cell culture.
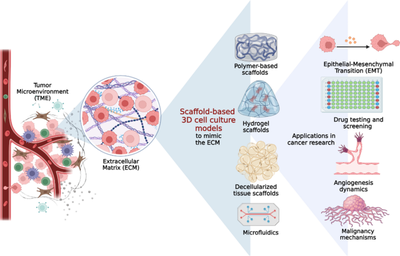
Cell culture has a lot to evolve and help different societies. One of the evolutions into the cell culture field is 3D cell culture, which can reduce the lack of complexity of the cells and structure problems. This can make the cells grow together in all directions into the media. This differs from the current 2D cell culture, which only grows on the bottom of the flasks. Organ-on-a-chip, which simulates human organs to test drugs and disease modeling. Additionally, stem cell-based therapies aim to regenerate damaged tissue and organs.
References:
1.https://info.abmgood.com/cell-culture-introduction
3.https://www.vanderbilt.edu/viibre/CellCultureBasicsEU.pdf
5.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2020.566607/full
6.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/molecular-biosciences/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2020.00033/full
7.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/physiology/articles/10.3389/fphys.2022.836480/full
8.https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.782766/full
